Many organizations struggle to connect their SEO efforts to actual business outcomes. This challenge becomes even more evident when multiple teams touch content, technical updates, design changes, or deployment cycles.
Google’s introduction of custom chart annotations in the performance report directly addresses this issue by allowing SEO teams and business owners to add meaningful context to their Google Search Console data. In this blog, you will learn why this matters, how to use it effectively, and how it can strengthen your overall Google search performance tracking.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhy Google Introduced Custom Annotations
Google rolled out custom annotations in November 2025 to help users understand the context behind spikes or drops in performance metrics.
For years, SEO professionals relied on third-party tools or spreadsheets to document changes. This led to gaps, mismatched dates, and confusion during reporting. With GSC performance report annotations, Google finally brought this documentation inside the tool where the data lives.
Additionally, this update builds on broader Google Search Console updates aimed at improving transparency. When you annotate key actions like publishing new content, updating metadata, fixing indexation issues, or launching link-building campaigns, you create a clearer understanding of your data trends.
Where You Can See Annotations Inside Search Console
You will find annotations at the bottom of your Performance report chart as small markers on the timeline. Hovering over any marker reveals your note.
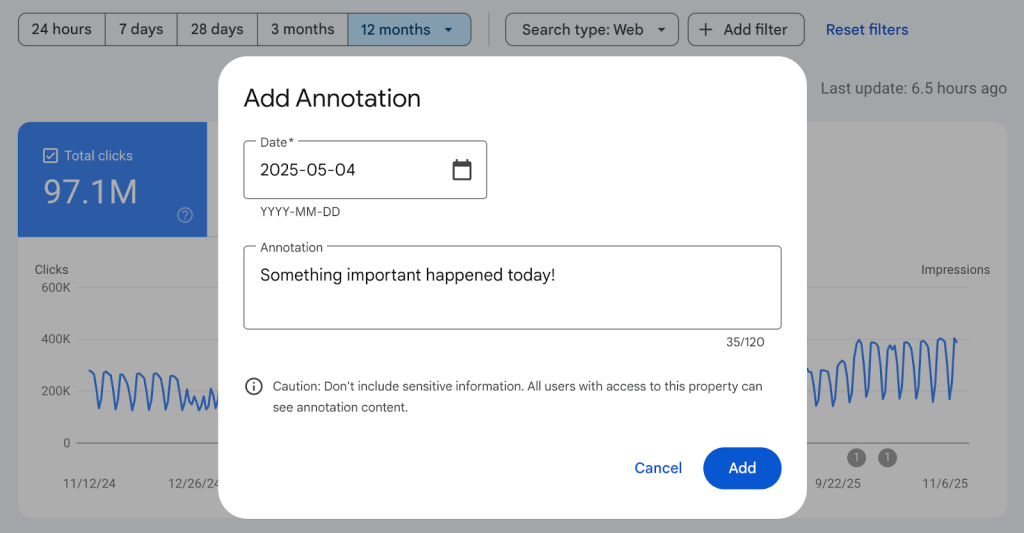
Image credit: Google for Developers
These custom chart annotations appear across filtered views such as device, country, and query filters, which makes them flexible and dependable for daily analysis. However, they do not appear in comparison mode or in 24-hour data filters.
Google also includes system annotations for events like reporting delays or data refreshing. These appear automatically, helping you distinguish between performance changes caused by your actions versus Google’s internal updates.
How to Add a Custom Annotation
Adding annotations is simple and quick:
- Open the Performance report in Google Search Console.
- Right-click on the date you want to annotate.
- Enter up to 120 characters describing what happened.
- Save the annotation to mark the date with a small indicator.
You can add up to 200 annotations per property, and older annotations beyond 500 days automatically expire.
You cannot edit an annotation once added. You can only delete it, so clarity and precision are essential.
Benefits for Reporting & Performance Tracking
1. Clearer Explanations for Performance Changes
With search analytics annotations, you no longer need to guess why your impressions dipped or clicks surged. The moment you deploy a new template, optimize schema markup, launch a promotional campaign, or add backlinks, you can annotate that date.
This creates a clear story behind your numbers and supports meaningful SEO reporting improvements.
2. Easier Collaboration With Teams and Agencies
If you’re working with an SEO agency, annotations serve as shared context for every update. This minimizes confusion, reduces repetitive questions, and speeds up reporting. Teams no longer need to cross-check multiple documents; everything is stored directly within Search Console.
Limitations to Know
While GSC reporting features are more useful than ever, they still have limits.
First, annotations auto-delete after 500 days, which means long-term analyses require additional documentation outside GSC.
Second, you cannot edit a note; only delete it.
Third, every user with property access can see your annotations, so avoid sensitive or internal-only details.
Despite these constraints, annotations remain an efficient way to enhance Google search performance tracking for businesses that prioritize data clarity.
Note: Anyone who has access to your Search Console property can view the custom annotations you add. Therefore, it’s best to avoid including confidential or personal details when creating them.
Conclusion
GSC performance report annotations help businesses move from vague assumptions to informed decision-making. By marking your major SEO actions, deployments, and technical changes, you add essential context to your data. As a result, your Search Console insights become more reliable, collaborative, and easier to interpret.
When paired with strategic support from a trusted SEO partner like 6S Marketers, known for expertise in link-building, content strategy, and SEO audits, you unlock even stronger reporting outcomes.
If you need help setting up a complete annotation strategy or improving your SEO reporting workflow, connect with 6S Marketers today.
FAQs
1. Who can see Google Search Console annotations?
Anyone with access to the property can view annotations, but only users with permission levels above “read-only” can create or delete them.
2. Are annotations available for all reports?
No. They are currently available only in the Performance report.
3. Can I edit an annotation after adding it?
No. You can delete an annotation, but editing it is not supported.
4. Do annotations affect ranking or indexing?
No. Annotations do not influence rankings. They only help with analysis.
5. What is the maximum number of annotations allowed?
You can create up to 200 annotations per property.
6. Which method should I use: Search Console UI or structured data markup?Use the Search Console UI for date-specific human notes. Use structured data markup when you want Google to understand events programmatically. They serve different purposes and work well together.



